

Disasters and accidents strike when they are least expected – and for people who lack the financial fallback to cushion against these unforeseen events, insurance can play a vital role in protecting the assets they worked hard for and the people they care for the most.
But insurance comes in different forms, and the key to finding the policy that fits one’s needs is understanding the type and level of coverage each one provides. In this article, Insurance Business explains everything there is to know about this essential financial instrument, so that your customers and potential clients can be armed with the proper knowledge to choose the best coverage possible.
This is part of our client education series, and we encourage insurance agents and brokers to share this article with customers to help them navigate this crucial financial tool.
Insurance serves as a financial cushion in the event something bad happens to the insured person – also referred to as the policyholder – and their assets.
Merriam-Webster defines insurance as a form of “coverage by contract whereby one party undertakes to indemnify or guarantee another against loss by a specified contingency or peril.”
In layman’s terms, insurance is a written contract between a person and the insurance company that puts the responsibility of paying for losses that the insured incurs on the insurer. This is given that the incident is specified as a covered event and the policyholder meets regular payments.
In the event a fire destroys a house, for example, home insurance will cover for the costs to repair and rebuild the property. If a person causes a vehicular accident, meanwhile, auto insurance can pay out for medical bills and third-party property damage resulting from the collision. If a policyholder dies, their loved ones can receive a financial benefit through their life insurance plan.
But what’s paradoxical about insurance is that people are paying for something that they are hoping they would never use. Skipping coverage, however, risks putting them and their family in dire financial straits should an unfortunate event occur.
How insurance works varies significantly, depending on the policy and insurance provider. Regardless, all policies come with four main components that policyholders need to be aware of to ensure that they are getting the right coverage. These are:
When purchasing an insurance policy, the first step a person needs to take is to apply and get approved. As part of this process, insurers evaluate how much risk they bring – meaning the likelihood that they will make a claim. From this, insurance providers calculate how much policyholders need to pay for coverage. This amount is called the premium.
Several factors come into play when determining premiums:
Once approved, the policyholder will need to make payments regularly. Insurers often give the insureds the option to pay on a monthly, quarterly, semi-annual, or a yearly basis. It is crucial that they meet regular premium payments as failure to do so may affect their eligibility come renewal time or even void their coverage.
Once the policy is active, it will remain in-force for a set period, called the policy term. At the end of the term, policyholders usually have two choices:
Many policyholders also use the second option to get cheaper rates, but that’s not the only way to save on auto insurance premiums, among other insurance types.
If they experience a covered event during the policy term, they will need to file a claim to notify the insurance company about what happened and provide documentation as proof. The insurer will then investigate to determine the validity of the claim, and if it is, the provider will pay out for the losses. We will discuss the insurance claims process more deeply in a separate article.
The policy limit of an insurance plan refers to the maximum amount the insurer will pay out for specific claims. It is often listed on the policy document’s declaration page, which outlines the key details of the insurance contract.
There are several types of policy limits. These include:
In some policies, policyholders are allowed to choose a limit. Others follow the requirements imposed by the government or an industry body. These include uninsured or underinsured motorist coverage in several states in the US.
Higher maximums also result in more expensive premiums. If a claim exceeds the policy limit, the insured may have to cover the additional expenses on their own.
A deductible is the amount that the policyholder must shoulder before the insurance company pays out a claim. Depending on the type of policy, deductibles can apply per policy or per claim.
Insurers typically impose deductibles to avoid having to reimburse a barrage of small and low-value claims. Policies with high deductibles often have lower premiums. Some industry insiders also suggest policyholders choose higher deductibles to save on insurance costs but cautioned that the amount must be set at a level that they can afford to pay.
Individuals and businesses searching for some form of financial protection can choose from a diverse range of insurance policies, with each catering to different clients’ unique set of coverage needs. This section details what the most popular types of insurance available in the market cover.
To operate a vehicle, it is almost always mandatory to carry car insurance. Getting caught driving without one can result in hefty fines and affect future eligibility for obtaining coverage.
Auto insurance is designed to protect motorists against financial losses in the event of accidents or theft. It does so by providing the following coverages:
There are a number of factors which go into choosing which type of insurance is required, often coming down to legislation in different countries, and even in different provinces and states within those countries.
Home insurance, also referred to as homeowners’ insurance, is not required by the law. Most lenders, however, set it as a condition for taking out a mortgage. Homeowners’ insurance may work differently, depending on several factors, including where the house is located, but most offer the following coverages:
Given that the home is often one of the biggest financial investments people have, it is wise to have some form of protection.
Health insurance policies are aimed at helping policyholders offset the costs of medical treatment by covering a portion of the professional and hospital fees incurred.
According to the US government’s health insurance exchange website HealthCare.gov, this type of coverage comes in several forms designed to meet the varying needs of the insured. These are:
Health insurance plans are also offered in four categories based on how the costs are split between the policyholder and the insurer. These are Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum, which are also referred to as the “metal tiers.” Here’s how the costs are split, according to HealthCare.gov.
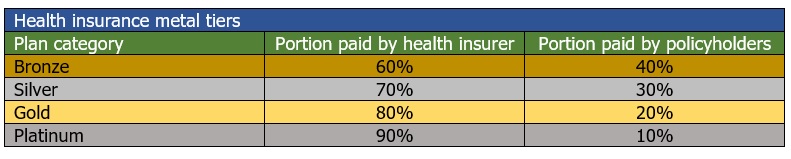
The example above is for the American healthcare system. Many countries have different types of coverages that are part of a single payer healthcare system, or universal coverage, depending on where you live. Your health insurance needs can vary widely depending on your country.
Often confused with health insurance, life insurance plans provide a tax-free lump-sum payment to the policyholder’s family after they die. Coverage comes in different types but generally falls into two categories, with each type offering different levels of protection. These are:
Term life insurance
This type of policy covers the insured for a set term. It pays out a stated amount, called a death benefit, if the policyholder dies within a specified period. This means they can only access the payment in the years that the plan is active. Once the term expires, the insured has three options:
Permanent life insurance
Unlike term life insurance, a permanent policy does not expire. Coverage is available in two main types, which combine the death benefit with a savings component.
A life insurance policy covers almost all types of death, including those due to natural and accidental causes, suicide, and homicide. Most policies, however, include a suicide clause, which voids the coverage if the policyholder dies by suicide within a specific period, usually two years after the start of the policy date.
An interesting aspect of life insurance you may not be aware of, is its ability to both protect and build your wealth. It is a much more useful form of insurance than most people realize.
By now, it should be clear how important insurance is in protecting people and businesses financially. Having the proper coverage can help policyholders recover faster from unforeseen accidents and calamities by providing the monetary means to rebuild their lives. But one of the biggest benefits of taking out insurance is having the peace of mind of knowing no matter what happens, you are financially protected.
Insurance plays a vital role in the lives of individuals, businesses, and various entities by ensuring protection against unforeseen events and uncertainty. With a primary objective to safeguard policyholders from substantial financial hardships, insurance acts as a safety net, effectively managing and reducing risks.
Policyholders establish agreements with insurance companies, paying monthly premiums in exchange for transferring certain risks to the insurer. Should covered losses occur, insurance companies fulfill their commitments by promptly paying claims, enabling policyholders to recover or replace their valuable assets.
The decision to obtain insurance offers individuals a profound sense of security. Insurance assures them of having reliable fallback options during challenging times. This peace of mind empowers individuals to plan for the future without constant worry.
So, what is insurance and what is it for? It’s a fundamental financial tool that protects individuals, businesses, and entities from the unexpected, allowing them to navigate uncertainties with greater confidence. Whether it be safeguarding personal possessions, ensuring the financial stability of loved ones, or shielding businesses from potential liabilities, insurance is an essential component of any comprehensive risk management strategy.
Insurance provides a variety of substantial advantages, including risk reduction, financial stability, business continuity, psychological alleviation, and asset protection.
Insurance protects against unforeseen events, mitigating the financial impact of occurrences such as automobile accidents, natural disasters, and health problems.
Insurance functions as a safety net, providing policyholders with funds to cover significant expenses in times of need, thereby ensuring a seamless recovery without financial strain.
Insurance compensates businesses for property damage, liability claims, and unforeseen events. This allows them to continue operations and maintain stability.
Knowing that one is protected by insurance reduces anxiety regarding financial losses and the unpredictability of future events.
Insurance protects valuable assets such as homes, vehicles, and personal property against potential damage and losses.
What is insurance and what are the benefits? Having insurance coverage gives individuals and businesses mental relief, knowing that they have a safety net in the event of unforeseen problems. It allows them to confidently plan for the future and navigate uncertain situations. Policyholders receive access to these benefits by sharing risks with insurance firms, which aid in their recuperation and growth in life.
Insurance policies typically do not provide coverage for damages resulting from fraud, negligence, normal wear and tear, pre-existing illnesses, conflicts, or nuclear injuries.
Intentional damages caused by the insured or any other malicious behavior are not included in insurance coverage. The normal usage and aging of insured assets, such as machinery or motors, are usually no longer covered.
Medical expenses related to pre-existing illnesses may not be covered by your medical insurance plan.
Damages arising from acts of war, terrorism, or nuclear accidents are generally no longer covered by insurance regulations. Losses that occur outside the geographical scope or time period specified in the policy may also not be insured.
To avoid confusion during the claims process, policyholders should thoroughly read their policies and become familiar with the listed exclusions. While insurance is essential for protecting against various risks, these exclusions are necessary to maintain the integrity of insurance and prevent misuse of coverage.
Insurance companies may offer additional options or riders to help policyholders protect themselves from risks that are not covered by the basic policy. By understanding these limitations, both individuals and organizations can choose the most suitable coverage policies to meet their specific needs.
In the realm of insurance, the transfer of risk goes from the policyholder to the insurance company. The insurance company assumes the responsibility of compensating for losses as outlined in the policy's terms and conditions.
When individuals or businesses purchase insurance coverage, they enter into an agreement with the insurance company. This agreement stipulates that the policyholder will make regular premium payments in exchange for the coverage provided by the insurance policy. By doing so, the policyholder transfers the financial risk associated with specific activities or events to the insurance provider.
Upon accepting the policyholder's premium payments, the insurer takes on the responsibility of reimbursing the policyholder for covered losses. The insurance company pools the premiums collected from multiple policyholders to create a fund that can be utilized to pay out claims when necessary.
This mechanism of sharing risk is crucial in the insurance industry. It allows individuals and businesses to safeguard themselves against potential financial hardships resulting from unforeseen events such as accidents, natural disasters, and health issues. Without insurance, individuals would bear the entire burden of economic losses, potentially leading to significant financial strain and difficulties in recovery.
To conclude, insurance companies assume the risk by providing financial protection and reimbursement to policyholders in the event of covered events. This transfer of risk mechanism offers policyholders the support they need to navigate uncertainty and recover from losses.
Do you still have questions? Be sure to get in contact with the insurance broker who sent this article to you, or refer to our Best of Insurance awards for help.
How about you? Do you think insurance is an important financial instrument? Use the comment section below to share your thoughts.
