

Car insurance is designed to protect you financially if you get involved in an accident or your vehicle gets stolen. While this may seem straightforward at first glance, there are several layers to this type of policy that you need to understand to access the best coverage possible.
Insurance Business explains everything you need to know about car insurance to help you find the right coverage. We will dig deeper into how this policy works in each state, what factors influence premiums, and how you can find the best rates.
If you’re looking for an auto insurance policy that matches your needs, this guide can help. We also encourage insurance professionals to share this article with their clients to assist them in their search. Read on and find out how you can be properly protected in this car insurance guide.
The Insurance Information Institute (Triple-I) defines car insurance as a contract between you and the insurance provider. That contract protects you against financial losses incurred because of an accident or theft.
This policy offers three types of coverage:
Car insurance is mandatory in almost all states, but the laws vary. We will discuss the different state requirements in more detail later.
Read more: What insurance is required by law in the US?
Most policies are issued semi-annually or annually, after which you need to renew yours.
Your car insurance plan can cover you and other family members listed in the policy. In some cases, it also provides coverage for those not listed in your plan but have permission to drive your vehicle. Similarly, it protects you if you are driving another person’s car – as long as you have permission, of course.
Car insurance, however, applies only for personal driving such as running errands, going on road trips, and commuting to and from work. It doesn’t cover business-related activities. If you’re using your car for commercial purposes, you need a separate kind of coverage, aptly called commercial vehicle insurance.
Commercial plans can also provide coverage if you’re using your vehicle to offer ride-sharing services. If you’re engaged in this type of business and planning to get additional coverage, it may be advisable to check with your insurance carrier first. The reason is that some personal car policies are extendable to cover ride-sharing services. Although this may come at an extra cost, it may be less expensive than taking out a standalone commercial policy.
Learn how liability car insurance can protect you in this guide.
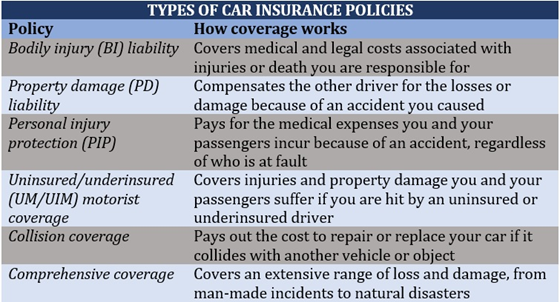
What makes car insurance a complex type of coverage are the varying requirements each state imposes. Depending on where you live, you may be required to take out a few or several policies. Here are the most common forms of auto insurance policies available.
Also called BI coverage, this type of policy is mandatory in almost all states. It helps pay for medical expenses resulting from injuries another person suffers because of an accident you caused. It also covers the legal costs if you’re sued due to the accident. Some policies pay out for lost income and funeral expenses.
Bodily injury coverage, however, doesn’t cover the injuries you or your passengers sustain. For these, you will need personal injury protection, which we will discuss later.
PD coverage is another car insurance policy that’s required in virtually all US states. It compensates the other driver for the losses or damage you caused in an accident. It also pays out the legal and settlement costs resulting from a lawsuit. Just like BI coverage, PD policies cover third parties, so it will not pay for the damage your vehicle sustains.
Also called PIP, or medical payments (MedPay) coverage in some states, this covers the medical expenses you and your passengers incur because of an accident. This is regardless of who is at fault.
Some policies also cover lost income if you’re unable to work, as well as the cost of household services if you can’t perform certain daily tasks. Coverage can also include a death benefit, which can cover funeral and burial costs.
PIP is sometimes referred to as “no-fault insurance” in reference to states with no-fault auto liability insurance laws, where this kind of coverage is mandatory. In these states, you are prohibited from suing at-fault drivers for compensation. This is unless the injuries you suffer are severe or your medical expenses have exceeded the state’s minimum requirement to sue.
You can learn more about this type of coverage in our comprehensive guide to personal injury protection insurance.
UM and UIM car insurance policies are often bundled together as they work almost the same. They are designed to fill the gap between the costs you incur and the at-fault driver’s ability to pay.
UM and UIM policies compensate for the injuries and property damage you and your passengers suffer if you are hit by an uninsured or underinsured driver. Coverage is also applicable to hit-and-run accidents.
You can find more details about this type of policy in our comprehensive guide to uninsured motorist coverage.
Collision coverage pays out the cost to repair or replace your car if it collides with another vehicle or object. Most policies also cover damage caused by potholes or if your car rolls over.
Collision insurance is an optional type of coverage, meaning you need to pay extra to add it to your standard car insurance. Most lenders and leasing companies set this type of coverage as a condition for your car loan or lease.
Collision insurance, however, doesn’t cover mechanical failure and normal wear and tear.
Comprehensive coverage is another optional type of car insurance. As the name suggests, it covers an extensive range of loss and damage. These include man-made incidents such as theft, arson, and vandalism, and natural calamities like storms, hail, and flooding.
Comprehensive policies don’t often cover vehicular crashes, which are already covered under collision insurance.
Here’s a summary of the common types of car insurance you can purchase.
If you want to know what kind of coverage the leading auto insurers in the country offer, you can check out our latest rankings of the top 10 car insurance companies in the US.
Car insurance is a must in almost all US states, but the minimum requirements vary. The table below details the minimum mandatory requirements in each state.
|
MINIMUM MANDATORY CAR INSURANCE LIMITS BY STATE |
|
|---|---|
|
State |
Minimum mandatory requirements |
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $50,000 per person BI: $100,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $15,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $15,000 per person BI: $30,000 per accident PD: $5,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $15,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $10,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident UM/UIM PD: $5,000 |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident BI: $10,000 per accident PIP: $15,000 per person PIP: $30,000 per accident |
|
|
PD: $10,000 per accident PIP: $10,000 per person |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $20,000 per person BI: $40,000 per accident PD: $10,000 per accident PIP: $10,000 per person |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $15,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 bodily injury liability per person BI: $50,000 bodily injury liability per accident PD: $20,000 property damage liability per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $20,000 per person BI: $40,000 per accident PD: $15,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident
PIP per person: $4,500 for medical expenses $900 per month to a year of disability or loss of income coverage $25 a day for in-home services $4,500 for rehabilitation-related expenses $2,000 for funeral, burial, or cremation expenses
Other: Survivor benefits of up to $900 per month up to a year for disability or loss of income and $25 per day for in-home services |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident PIP: $10,000 per person |
|
|
BI: $15,000 per person BI: $30,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $50,000 per person BI: $100,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $100,000 per accident MedPay: $2,000 |
|
|
BI: $30,000 per person BI: $60,000 per accident PD: $15,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $30,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $60,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $20,000 per person BI: $40,000 per accident PD: $5,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $20,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $40,000 per accident PIP: $8,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $20,000 per person BI: $40,000 per accident PIP: Unlimited Property protection: $1 million |
|
|
BI: $30,000 per person BI: $60,000 per accident PD: $10,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident PIP: $40,000 per person |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $20,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $20,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident UM/UIM PD: $25,000 MedPay: $1,000
Car insurance is not mandatory, but these are the requirements for those who opt in. |
|
|
PD: $5,000 per accident PIP: $1,000 per person |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $10,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $10,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident PIP: $50,000 personal injury protection per person
Other: $50,000 liability for death per person $100,000 liability for death per accident |
|
|
BI: $30,000 per person BI: $60,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $30,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $60,000 per accident UM/UIM PD: $25,000 |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident PIP: $30,000 per person |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $20,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident PIP: $15,000 per person |
|
|
BI: $15,000 per person BI: $30,000 per accident PD: $5,000 per accident MedPay: $5,000 |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $15,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $30,000 per person BI: $60,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $65,000 per accident PD: $15,000 per accident PIP: $3,000 per person |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $10,000 property damage liability per accident UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $100,000 per accident UM/UIM PD: $10,000 |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $20,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident UM/UIM PD: $20,000
Car insurance is not mandatory, but these are the requirements for those who opt in. |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $10,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $25,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident UM/UIM PD: $25,000 |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $10,000 per accident UM/UIM BI: $25,000 per person UM/UIM BI: $50,000 per accident |
|
|
BI: $25,000 per person BI: $50,000 per accident PD: $20,000 per accident |
|
Car insurance is not mandatory in two states: New Hampshire and Virginia.
In New Hampshire, the Financial Responsibility Law only requires drivers to provide proof of their financial capability to cover for injuries and damages if they cause an accident.
In Virginia, drivers can opt out of coverage if they can show evidence of financial responsibility. Those who choose to be uninsured, however, will need to pay a $500 uninsured motor vehicle (UMV) fee at the state’s Department of Motor Vehicle.
Although each state imposes its own minimum insurance requirements, you should remember that these are not always enough to protect yourself and your property. The answer to the question, “how much car insurance do you need” depends on a range of factors. These include where you live, what kind of vehicle you drive, and how much you can afford to pay.
Experts recommend taking out the highest amount of liability coverage that you can afford. If your finances allow, purchasing a 100/300/100 policy can provide you a high level of protection. This type of coverage consists of:
If your state doesn’t require PIP and UM/UIM coverages, these may still be worth considering. It may also be a good decision to take out additional coverages such as collision and comprehensive policies to protect your vehicle from unexpected incidents.
Because each driver comes with a unique set of risks, it is difficult to come up with a one-size-fits-all figure that accurately represents how much car insurance costs. To calculate premiums, insurers consider different factors that indicate how much risk a driver poses.
The table below details some of the most common variables that insurance companies factor in when determining car insurance rates.

Your choice of insurance provider is another major factor that can affect your car insurance rates. If you want to find out which auto insurers in the country offer the best value for your money, you can do a side-by-side analysis through our car insurance comparison guide.
Car insurance is one of the biggest costs associated with owning and operating a vehicle. Because of this, going with an auto insurer that offers cheaper coverage can be tempting. But doing so comes with a caveat – you risk losing more, especially if the level of protection such policies provide is inadequate.
To get the most out of your car insurance, you need to understand the different options available and the quality of coverage these policies offer. Our comprehensive guide to finding cheap car insurance gives you practical tips and strategies on how to access lower premiums without sacrificing quality.
Given a choice, would you still take out car insurance or not? Do you think the premiums you pay for coverage are worth every cent? Feel free to share your thoughts below.
